Introduction to Embedded Systems Design
We have been brought up in the age of computing.Computers are everywhere (some we see, some we do not see).
Types of computers we are familiar with:
- Desktops and Laptops
- Servers
- Mobile phones
But there’s another type of computing system that is often hidden.
- Far more common and pervasive...
- Hidden in the environment.
What are Embedded Systems?
Computers are embedded within other systems:
What is “other systems”? – Hard to define.
- Any computing system other than desktop / laptop server.
Basic Definition
It is a microcontroller or microprocessor (Arduino Or Raspberry Pi) based system that is designed to control a function or range of functions, and is not meant to be programmed by the end user.
- The user may make choices concerning the functionality but cannot change them.
- The user cannot make modifications to the software.
Typical examples:
- Washing machine, refrigerator, camera, vehicles, airplane, missile, printer.
- Processors are often very simple and inexpensive (depending on application of course).
Billions of embedded system units produced yearly, versus millions of desktop units.
Common Features
- They are special-purpose or single-functioned.
- Tight constraints on cost, energy, form factor, etc.
- They must react to events in real-time.
They have Typical Design Constraints
- Low Cost
- Low Energy Consumption
- Limited Memory
- Real-Time Response
Basic Operation of a Computing System
The central processing unit (CPU) carries out all computations.
- Fetches instructions from the program memory and executes it; may require access to data in data memory.
The input/output block provides interface with the outside world.
- Allows users to interact with the computing system, and also observe the output results.
About the instruction set architecture (ISA) of the CPU.
- Complex Instruction Set Computer (CISC): Typically used in desktops, laptops and servers (courtesy Intel)
- Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC): Typically used in microcontrollers, that are used to build embedded systems.
Broadly Two types of architectures:
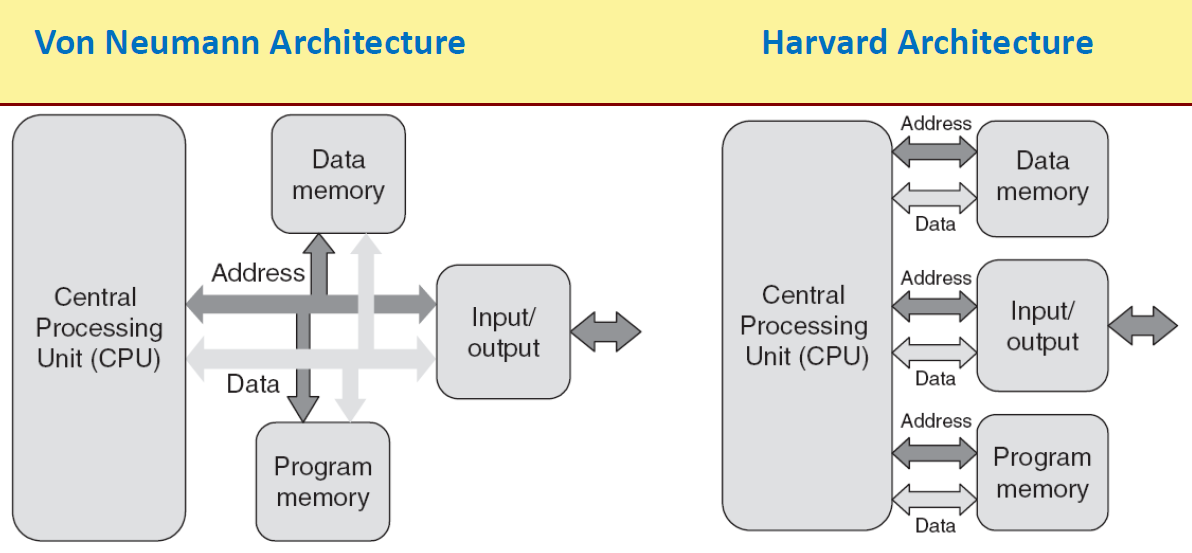
Von Neumann Architecture
- Both instructions and data are stored in the same memory.
- This model is followed in conventional computing systems.
Harvard Architecture
- Instructions and data are stored in separate memories
- Typically followed in microcontrollers, used for building embedded systems.
- Instructions are stored in a ROM (permanent), while temporary data are stored in RAM.
What is a Microprocessor?
It is basically the entire CPU fabricated on a single chip.
- Consists of a set of registers to store temporary data.
- Consists of an arithmetic logic unit (ALU), where all arithmetic and logical computations are carried out.
- Consists of some mechanism to interface external devices (memory and I/O) through buses (address, data and control).
- Consists of a control unit that synchronizes the operation.
Microcontrollers: The Heart of Embedded Systems
It is basically a computer on a single chip.
- Very inexpensive, small, low power.
- Convenient for use in embedded system design.
It operates on data that are fed through its serial or parallel input ports, controlled by the software stored in on-chip memory.
- Often has analog input pins, timers and other utility circuitry built-in.

